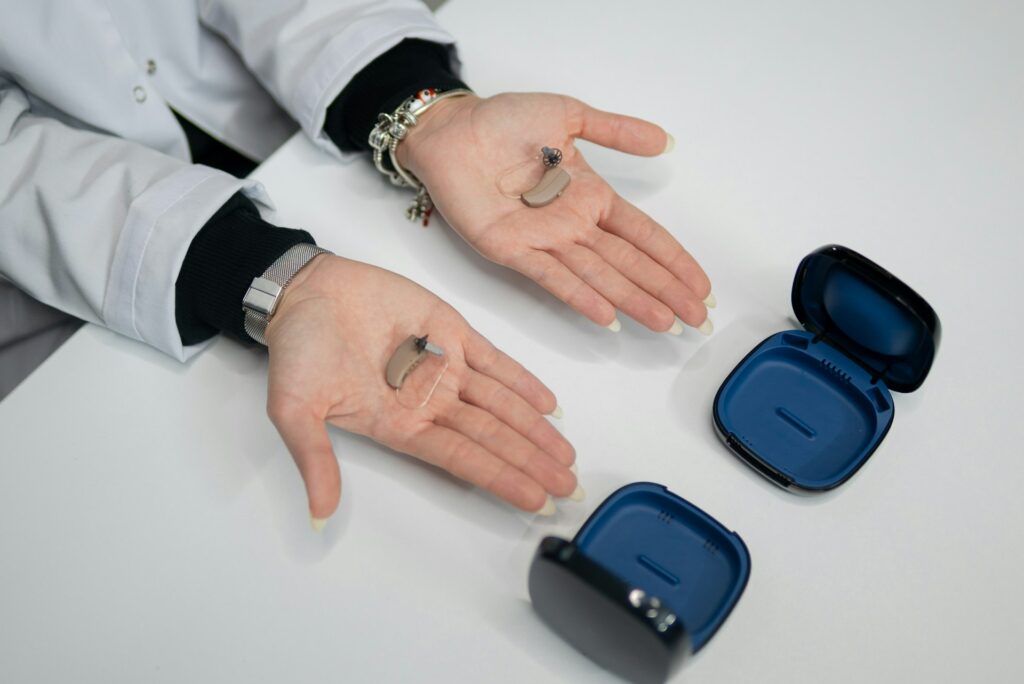
Hearing loss is a common problem that affects people of all ages. The signs of hearing loss can vary reliant on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, you may only experience a slight reduction in the ability to hear certain sounds. In more severe cases, you may not be able to hear anything at all.
Hearing loss may result from a variety of causes. Some are transient, and others are long-term. But almost all can be treated with the assistance of a knowledgeable hearing care facility. When you have hearing loss, you must get medical help immediately. The benefits of keeping your hearing are numerous, and treatment is frequently painless.
Hearing loss has been connected to several illnesses, such as mental health decline, from social isolation to balance issues to cognitive decline.
A hearing test or examination by a healthcare professional like an audiologist can reveal a “sign” of hearing loss. What you observe but may not be able to measure is referred to as a “symptom.”
How Does Hearing Loss Occur?
- Ageing
- Infected ears
- Head trauma
- Headphones with a loud volume
- Exposure to specific drugs or substances
- Years of being in noisy environments
Common Symptoms
Depending on the kind you have, the signs of hearing loss can differ greatly. Temporary hearing loss may occur if we are exposed to loud noise for a lengthy period or if we are sick with the flu or a cold. Permanent hearing loss can appear suddenly and develop gradually. The following section covers these general hearing loss symptoms in more detail.
- Others remark your television or radio is on loud, and your speech is slurred.
- difficulty hearing loud noises, such as buzzers, alarms, doorbells, telephones, and birds
- requesting that others talk loudly, more clearly, or more slowly
- Tinnitus (ear ringing) (ear ringing)
- hypersensitivity to certain loud sounds
- An earache that ringers
- Speech is challenging to understand in noisy settings, such as public spaces.
Loss of Sensorineural Hearing
About 90% of those with hearing deficits experience this most frequent hearing loss. This occurs when the auditory nerve and cochlea are compromised, making it impossible for them to transmit electrical signals to the brain accurately. Almost generally permanent, sensorineural hearing loss develops gradually over time.
Human hearing can detect sounds between 20Hz (deep bass) to 20,000Hz (very high-pitched). We inevitably lose our hearing’s upper range as we become older. While dog whistles are typically above the usual adult hearing range, it is known that children may hear them. We can lose the ability to distinguish between different frequencies without losing our overall hearing when the inner ear is damaged or degraded.
High-Frequency Hearing Loss
High-frequency hearing loss makes it tough to hear sounds in the higher register of the auditory spectrum. Presbycusis, or hearing loss brought on by ageing, is frequently linked to this.
- Sounds from alarm clocks and timers, birds tweeting, or telephone rings are hard to hear.
- Voices with higher pitches, such as those of women and children, are more difficult to comprehend.
- You may mistake words because some syllables, such as sh, s, f, v, th, and p, are difficult to understand.
Noise Notch Hearing Loss
The loss of mid-high range frequencies, known as notch hearing loss, is a typical symptom of hearing loss brought on by noise. Even if you have trouble hearing voices with a higher pitch, you can still hear high-pitched sounds.
Mid-Range Hearing Loss
Less frequent than high-frequency hearing loss is mid-range hearing loss. It can become difficult to understand speech with background noise, and discomfort from loud sounds can happen.
The sense that your hearing is not impaired but that your capacity to understand speech is deteriorating results from the possibility that you may still clearly hear low- and high-pitched sounds.
Low Frequency
Even less frequent. Men’s voices can be difficult to hear, while women’s and children’s voices are unaffected. You could also experience difficulty hearing someone when speaking on the phone but not in person. It’s possible that you won’t hear deeper environmental sounds like thunder or bass music. This hearing loss has been linked to Meniere’s disease in its early stages.
Conduction-Related Hearing Loss
Conduction-only hearing loss affects about 10% of those who have hearing loss. When the outer or middle ear isn’t working properly, but the inner ear is, it’s called conductive hearing loss.
The causes could be a head injury, an ear infection, a torn eardrum, fluid in the ear canal, abnormal bone growth in the middle ear, and blockage.
Surgery or medication is typically an effective treatment for this hearing loss. Even though hearing deterioration can happen more quickly than sensorineural hearing loss and exhibit similar symptoms, the cause is frequently simple to find.
Conclusion
Hearing loss is a serious condition that can impact day-to-day life. The signs and symptoms vary from person to person. However, some of the most common signs and symptoms are difficulty understanding speech, difficulty hearing in noisy environments, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ears. If any of these symptoms are present, it is important to make an appointment with a qualified audiologist to receive a hearing test and hearing aid. Early detection and treatment of hearing loss can help to reduce the impact on one’s quality of life.
Country Hearing Care Mildura provides hearing tests, hearing aids, balance issues, Hearing Aid Servicing, wax issues & more. Get expert hearing care today!